Health Care for Women
Early detection of cancer is done by screening. Common cancers found in women are breast cancer and cervical cancer.
Breast Cancer ScreeningThe most important step is breast self examination (BSE). It should be done every month before your period or, in menopausal women, on a fixed date of every month. Your physician should examine you every six months to one year. There are four methods for screening for breast cancer:
Breast Self Examination (BSE) It is important that your doctor teach you how to do BSE. A general description follows. BSE involves two parts: looking at the breast and feeling the breast.
Looking at the breast should be done either sitting or standing in front of a mirror in good light.
Step 1: Keep both arms by the side of your chest and look for:
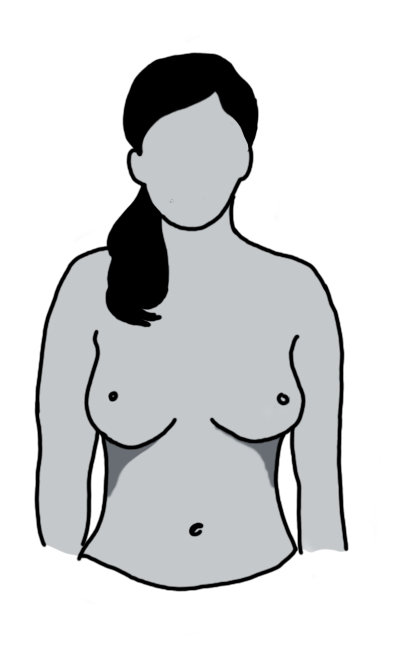
- Any change in contour or shape of the breast
- Dimpling or pulling of skin
- Dryness or rash around nipple
- Retraction of nipple
- Swelling, puckering or redness over breast
- Fluid leaking from the nipple.
Step 2: Raise both arms above or behind your head with locked hands.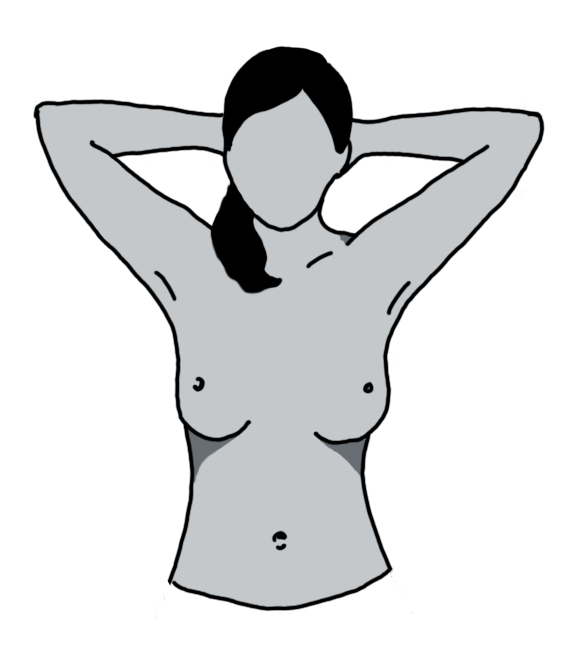
- Look for changes in breast contour/shape on both sides
- Nipple line should be horizontal. If there is any change, there may be an abnormality.
Step 3: Press both hands on your hips to make your breast prominent and look again for any change in size, shape or movement.
Step 4: Lean forward and see that both breasts are falling equally on both sides with prominent nipple.
Feeling the breast:
Lying position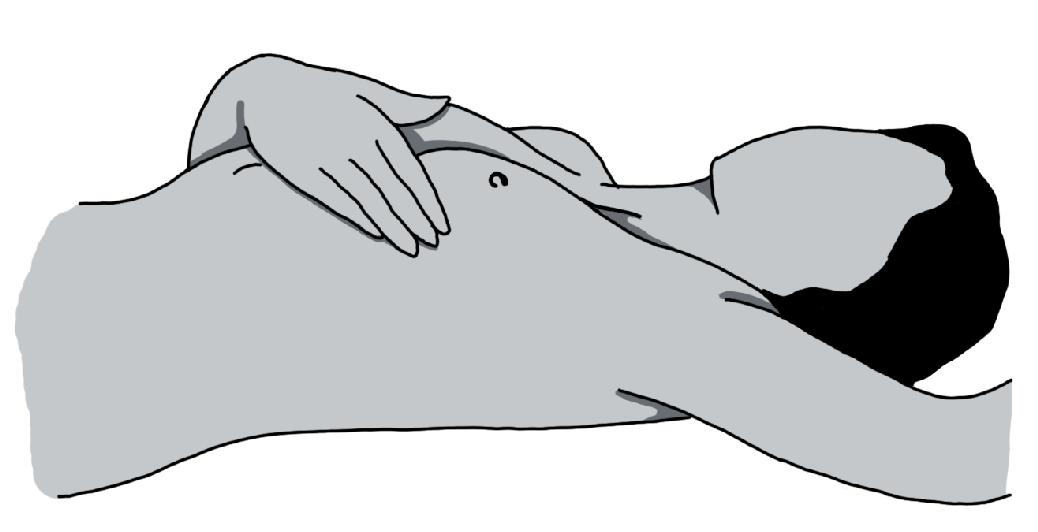 First lie on your back and a put a pillow or folded towel under the shoulder to raise your breast. Use the pads of your fingers of the opposite hand.
First lie on your back and a put a pillow or folded towel under the shoulder to raise your breast. Use the pads of your fingers of the opposite hand.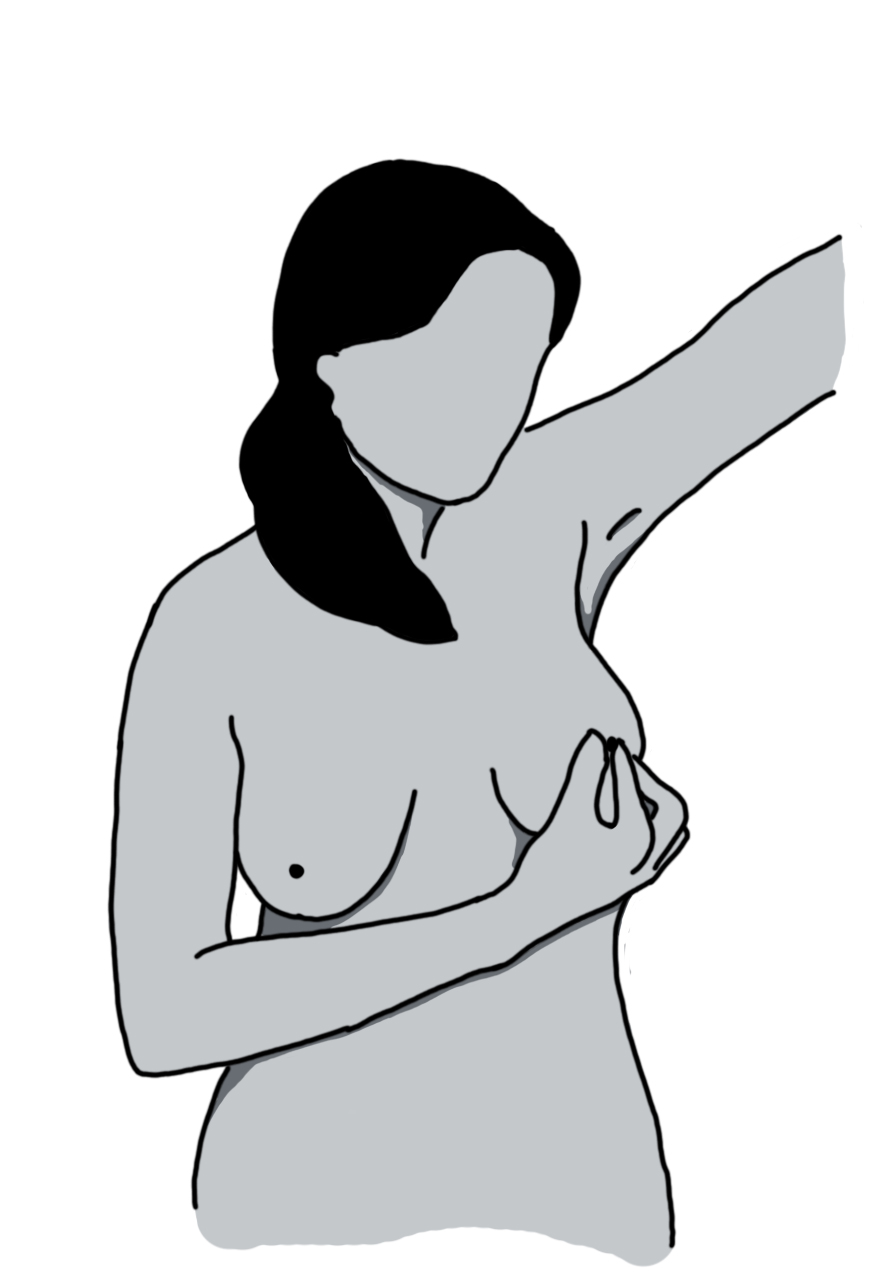 Gently rotate your fingers in circular pattern and press them gently to feel any lump, tenderness or irregularity in your breast.
Gently rotate your fingers in circular pattern and press them gently to feel any lump, tenderness or irregularity in your breast.Squeeze your nipple for any discharge. Clear, red, or dark brown discharge is abnormal.
Feel your breast towards the armpit. Feel in your armpit as well as your neck for any lump or swollen gland.
Repeat for the other breast.
Standing position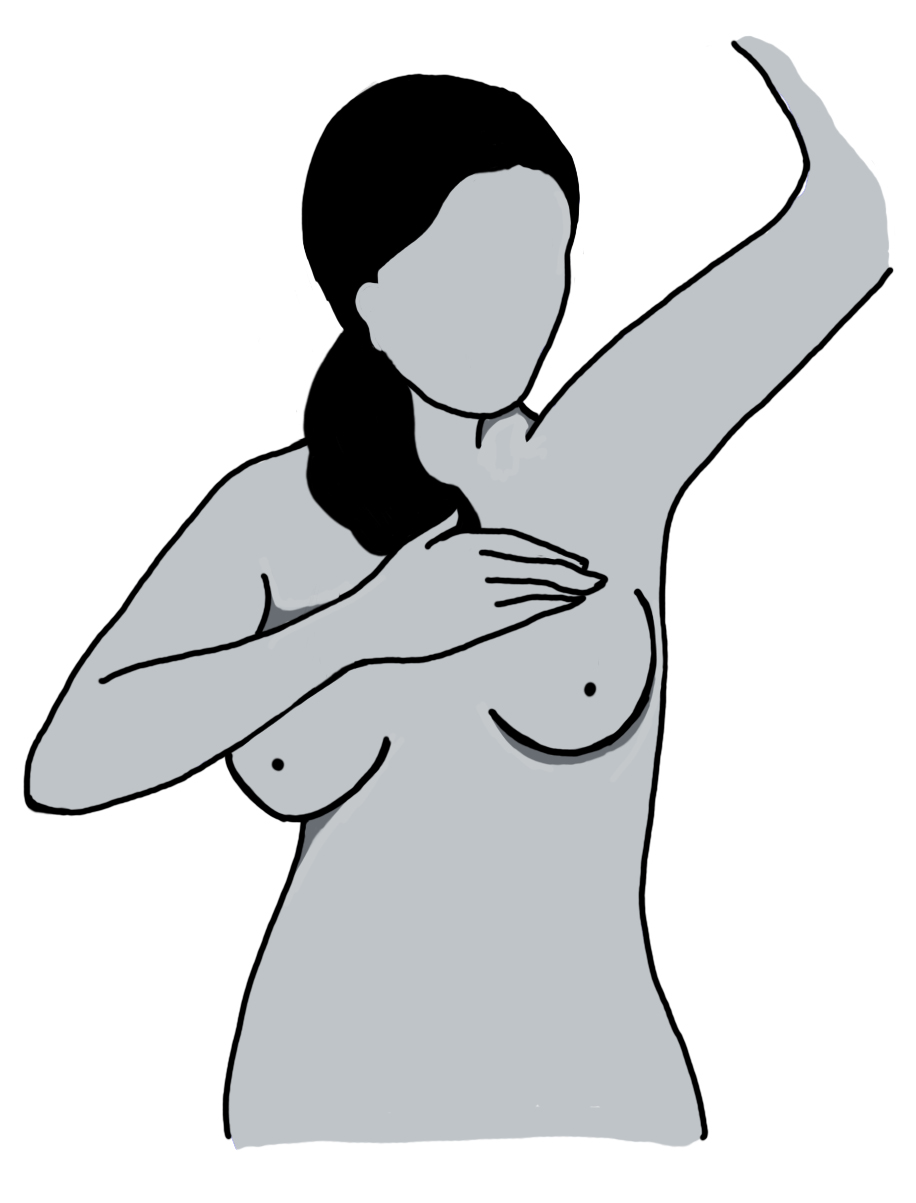 The same examination can be done while you are taking your shower as soapy and wet hands can more easily be moved over the breast and to feel deeper into the breast tissue. Try to make a habit of examining yourself during bathing.
The same examination can be done while you are taking your shower as soapy and wet hands can more easily be moved over the breast and to feel deeper into the breast tissue. Try to make a habit of examining yourself during bathing.- Mammography In case of any abnormality, mammography should be done at 30 to 35 yrs of age, then every 3 year interval between 40 to 50 yrs of age and after that every year.
- Sonomammography A non-invasive method for detection of fluid-filled lumps. It is safe during pregnancy.
- Fine-needle aspiration (FNAC) and core biopsy are methods used to further examine suspicious lumps.
- Many breast lumps are not cancerous (especially in women who have lumpy painful breasts before their periods.)
- Any hard or irregular lump, retracted nipple, bloody discharge from nipple, or puckering of breast skin should be shown to your physician immediately. If you notice any abnormalities in one or both breasts, visit your doctor or local hospital.
- Risk factors for breast cancer include: older age at first pregnancy, older age at last pregnancy, no childbirth, no breast feeding, and gaining weight as you age.
- A healthy lifestyle without stress, maintaining a steady weight, regular exercise, eating lots of high fiber green, yellow, orange, and red coloured vegetables and fruits can help in preventing cancer.
- If a close family member has had breast cancer, you may be more likely to get it. So, be vigilant.
Cervical cancer occurs mainly in women who are or have been sexually active.
The following may increase the risk of cervical cancer:- Early sexual life, i.e., sex before 20 years of age.
- Multiple sexual partners – or partners who, themselves, have had multiple partners.
- Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) infection.
- Smoking & other tobacco consumption.
- Repeated pregnancies, abortions &deliveries.
- Penile cancers in husbands or partners.
- Poverty, low socioeconomic status, and poor personal hygiene.
- Immunosuppression such as is caused by HIV infection.
Clinically, cervical cancers initially do not cause symptoms, but can be detected by having a regular Pap smear test and examination.
A Pap smear is taken from the neck of the womb with the help of a wooden spatula or brush. The watery smear is then spread evenly on a glass slide which is then stained (Papanicolaou stain) to make the cells easier to see. The slide is viewed under the microscope by a doctor or expert technician to detect any abnormal cancer cells.- A Pap smear should be done yearly in all sexually active women.
- First Pap smear should be at 2l years of age.
- From the ages of 20 – 30, repeat every two years.
- For those 30 and above, repeat every 3 years
- Screening can be stopped after 65 years of age if three consecutive smears are normal.
- Women who have had a complete hysterectomy for reasons other than cancer do not need further Pap tests.
Colposcopy. All smears that show evidence of HPV infection should be followed up by colposcopy – direct visual examination of the cervix. A biopsy will be taken from any suspicious-looking area and examined for cancer.
Please Remember:If you have any of the following symptoms or signs, you should contact your doctor immediately.
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse, bleeding between periods, bleeding after menopause.
- Offensive vaginal discharge.
- Unexplained vulval lumps or thickening.
- Vulval itching, white patch, or ulcer.
With grateful thanks to www.breastcancer.org; this has been adapted for local women.